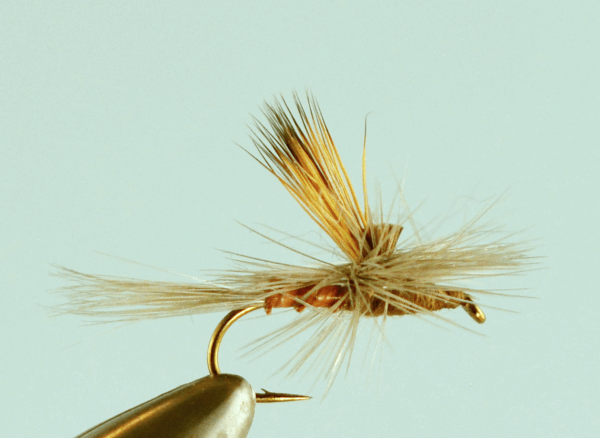
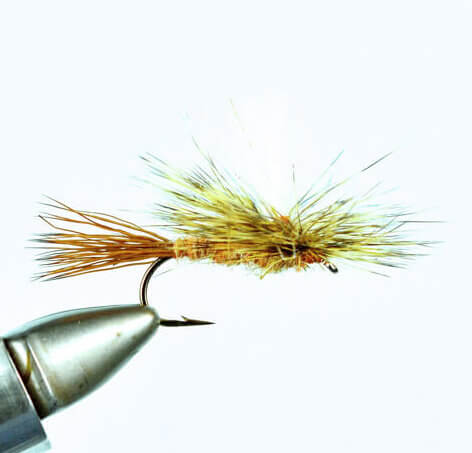
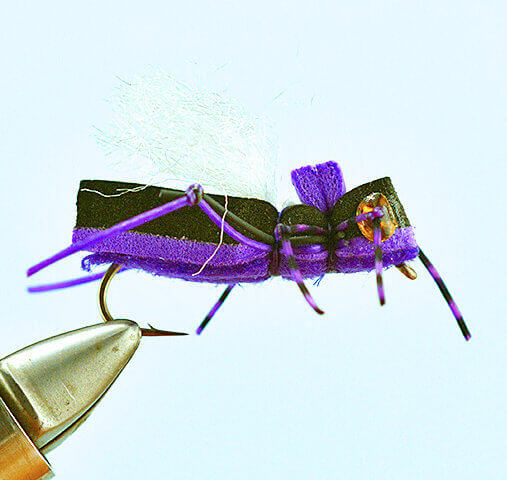
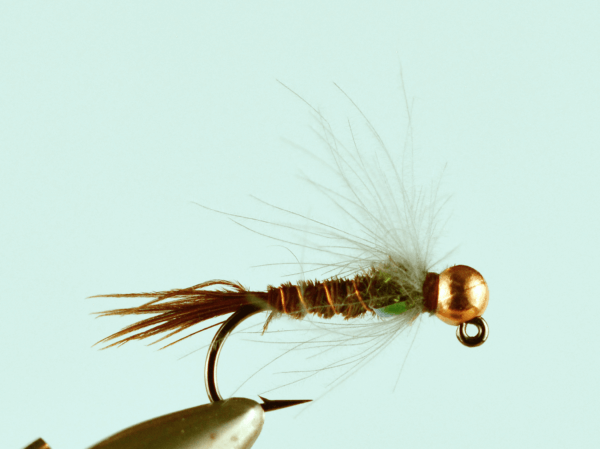
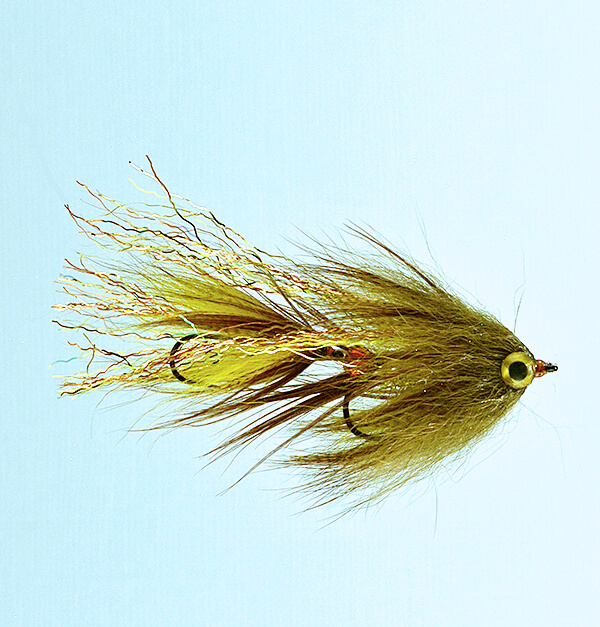
Lets start by saying the Missoulian Angler is at the far right on the bell curve. If left is the very casual angler, center is Missoula’s standard out fly fishing 50 days a year, we live on the far right. And if you bell curved the far right, we’d STILL be far right!
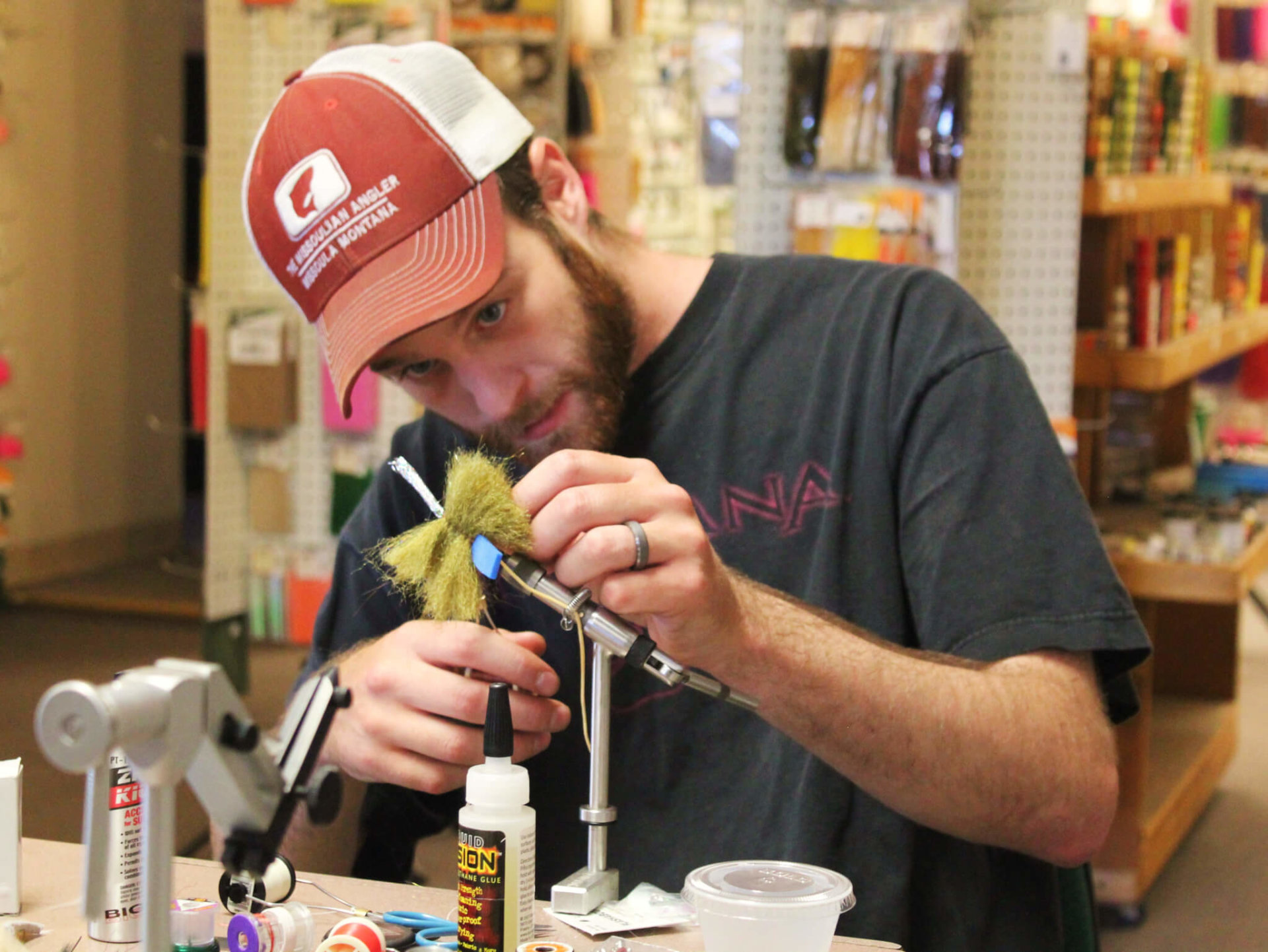
All our employees tie flies. Most have been professional tyers, and we all tie flies for the shop.
We started the same way. Someone told us we might be able to save money by tying flies (HA!) or there was a purer joy in catching fish on a fly you tied yourself (true). Now, we tie because we don’t know any other way.
It’s been said that every fly you tie is a little bit of hope for the season. Every wrap of thread is a plan for the next time you hit the water. And let’s not make any bones about it- you think you can build a better mousetrap! As you bend the materials onto the hook, you can’t help but wonder if THIS is the fly that will turn your season around. That’s what fly tying is about . . .
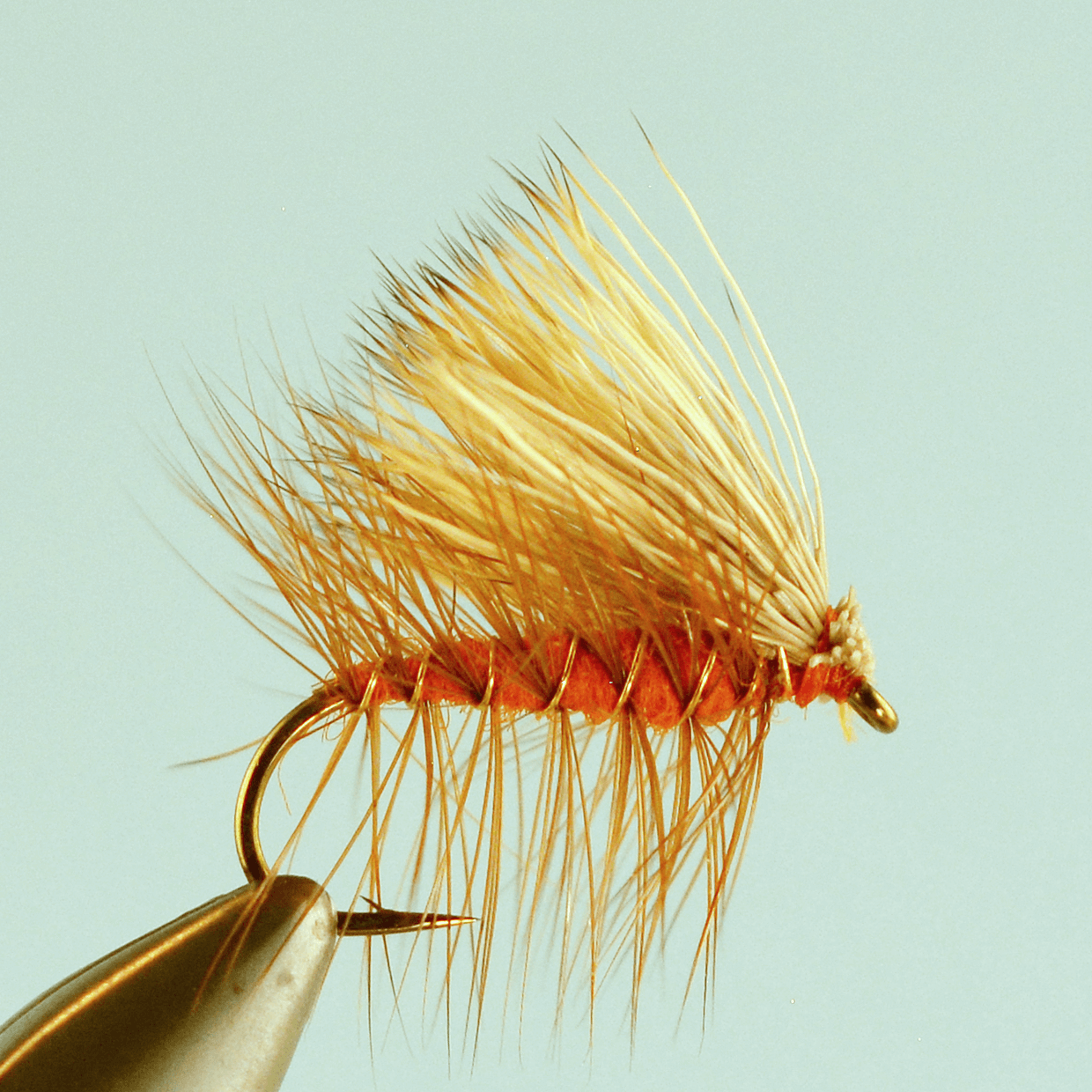
But it doesn’t happen over night, and there’s the rub. Customers come in all the time and say, “I want to tie the Sex Dungeon and the Royal Wulff. Those are my two favorite flies and I’m always out of them.” We always respond with tying flies is great, but you may need to set your sights a bit lower to start. How about a Pheasant Tail Jig and a Pat’s Rubberlegs? Sometimes it’s yes, and sometimes it’s no.
Because fly tying isn’t an art- it’s a hand skill, like hitting a baseball or knitting a sweater. For the same reason you don’t learn to hit facing major league pitching, or start knitting with a multi color, zipper back pant suit, you have to start easy in fly tying. Choose two simple patterns, and start to tie them, like a Pheasant Tail Jig and a Pat’s Rubberlegs! You’ll need tools for tying flies, a place to tie, and the time to spend behind the vise.
And here’s what you get when you start to tie flies. Complaints from your significant other that there’s fuzz all over the house. A bunch of flies that look nothing like the picture on Instagram. Small punctures on the ends of your fingers where the hook inexplicably ended up. A much more varied and colorful way to express yourself when the thread breaks for the 3rd time on one fly. You’ll be in closer contact with your fly fishing buddies, all asking you for “just a couple” of your best bugs. You wonder what possessed you to even start this silly habit.
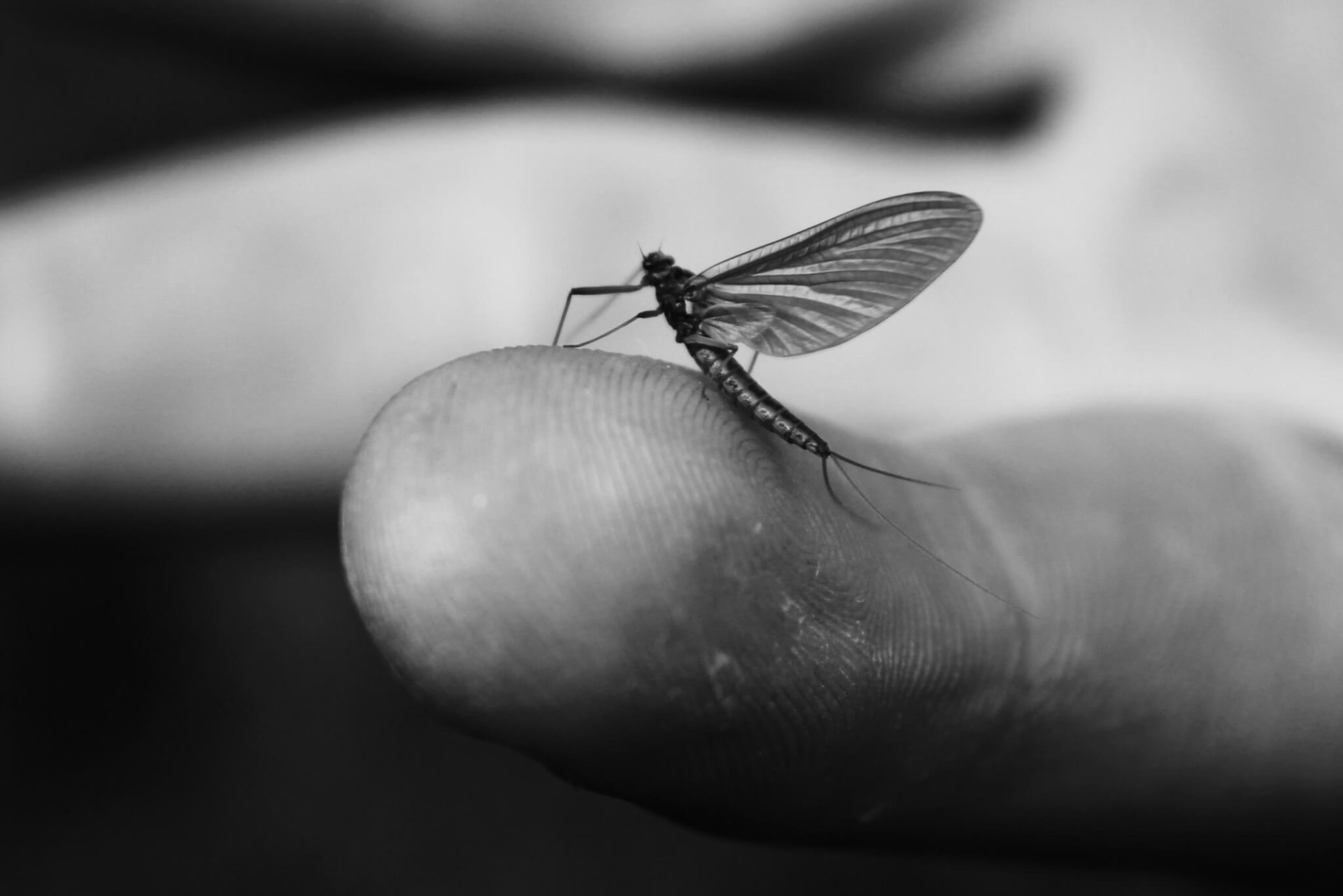
Until you start to see the other side of the coin. It’s more subtle and far reaching, and it doesn’t come immediately. The moment you tie your first Pheasant Tail, you have to think about proportions. The Abdomen is 60% of the body- the Thorax is 40%. Next thing you know, you find out all mayflies have the same proportions, they just vary in size. Pretty soon, you’re looking under rocks and seeing that the flies you’ve been tying aren’t exactly the right color, so you modify that. Your bugs start to look better to the fish.
All of sudden, the shucks on the side of the river begin to mean more. You’re looking at size and shape, and now comparing it to what you’re making. You begin to make changes to your flies, and they begin to work better.
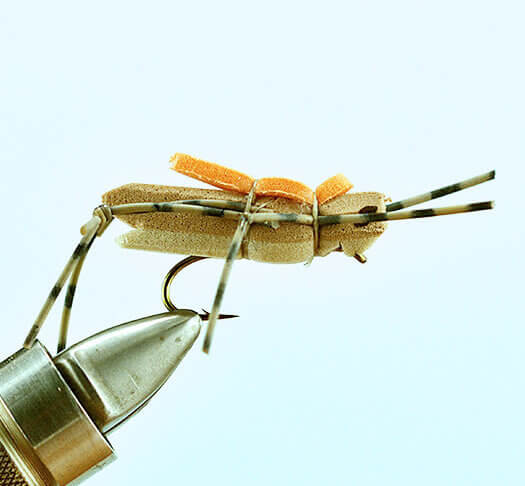
A grasshopper flies by, and it’s no longer just a hopper. You start to notice the hoppers are different sizes. Some have bright red legs, some don’t. They vary in color, and even a bit in shape. Some have very prominent legs, some are smaller. All this goes into the hopper (get it?!?!) and the next time you’re at the bench, you start to make adjustments to your patterns. They start to look more like a hopper you see on the water, not what others think a hopper should look like. You begin to scope the internet, looking at hopper patterns. You see things you like, you see things you don’t like. You begin to steal like an artist!! You take a body from one hopper and the wings from another. Legs from a third and a head from a fourth. You’re observing things as you’ve never done, and now you’re mixing and matching, learning more every time about what a hopper is and isn’t to a fish. Not all will work, but with every modification, you get closer to a hopper that works for you, that you have confidence in.
That’s the real secret about fly tying. Not that you’ll have flies when you need them, not that they’re better tied and more durable. The real secret of fly tying is now you know so much more. You’re looking at the naturals with a brand new and critical eye. They’re no longer random bugs. You’re no longer reading a fishing report and wondering what it all really means. Without knowing it, you’re learning about insect life cycles, and how and where trout interact with them. You’re seeing how the river works- how water, insects and trout all come together. Wait till you find out about clingers, crawlers and burrowers. All of a sudden, a riffle makes more sense. It’s the breeding ground for insects. No wonder trout stack up in there. You’re a better angler.
All because you took your fly fishing indoors. The moment you set up the vise for the first time, and started bending thread to hook, you’re taking giant steps to be ahead of the curve. Soon, you’ll be looking back and wondering how did I ever catch a trout? I had no real clue what was going on on the river! If you really get the bug (get it?!?!) you’re going to expand your pattern listing. You’re going to take some chances with new and different flies- always with the knowledge you’ve earned, knowing they have a very good chance of working. You’re a smarter angler, you’ve traveled further right on the bell curve.
It’s all about success on the water. At the Missoulian Angler, we learn as much from our customers as they learn from us. A fisheries biologist told us that when minnows hatch, they have no air in their swim bladder. They can’t swim until they surface and take in air. Before that time, they just sort of drift with the current. You have a Eureka moment. You have had nymphs taken as if they were a streamer. This explains it! The trout think it’s a minnow unable to swim. We all tied up some very thin, very small minnow imitations to be used under an indicator. They crush fish when the minnows are hatching. We learned more, and that made us more effective anglers.
Learning never stops on the water. It never stops at the vise either. Not just tying techniques and skill level, but that knowledge that seeps in while concentrating of fly fishing. Everything gets ratcheted up just a bit more, and keeps going. You find yourself stepping into the water with more confidence and greater skill. It’s an upward spiral that never really stops. We tell you that from our combined 100+ years of fly tying experience in the shop.
As the weather changes, and opportunities on the water get fewer and farther between, it might be a good time to think about taking your fly fishing indoors. You’ll thank us next year!